Below is a brief overview and guide to help you quickly familiarize yourself with the key features of Strand NGS. If you have any questions about a particular feature or experiment workflow, please contact us for more information or register for an interactive webinar. If you are interested in trying the software yourself, sign up for a trial license.
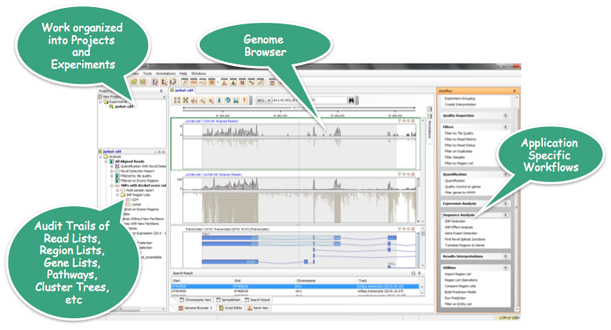
Strand NGS is built and supported by the same team of scientists and engineers that build GeneSpring®, Agilent Techologies' leading expression analysis platform used by several thousand researchers worldwide.
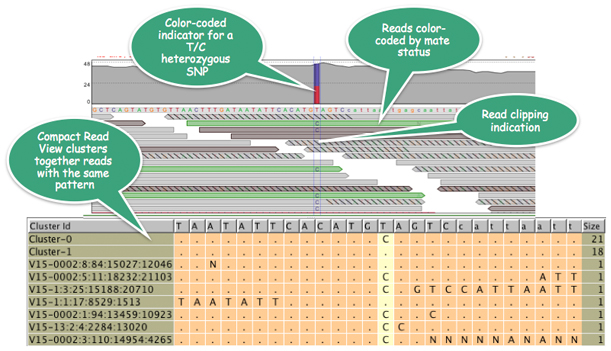
In the Yoruba genome (Bentley et al, Nature) with 3.5 billion reads, Strand NGS finds around 4m SNPs, 92% of which are known in dbSNP.
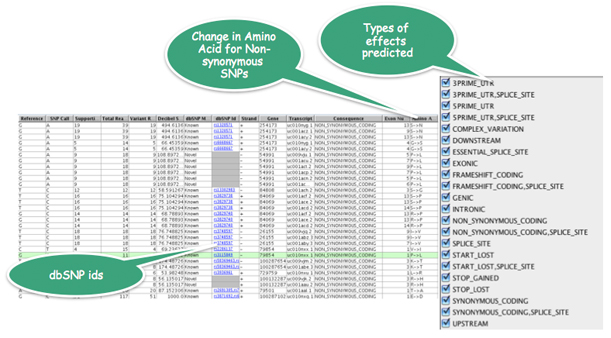
Strand NGS identifies roughly 110 genes which gain a STOP codon in the Yoruba genome (Bentley et al, Nature).
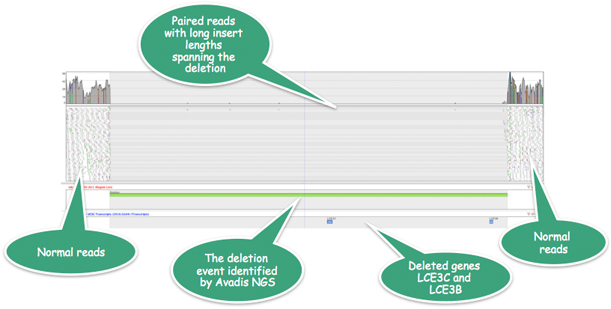
In an anonymous genome, Strand NGS identifies a 32KB homozygous deletion that is known to result in susceptibility to Psoriasis (see http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2350/11/45).
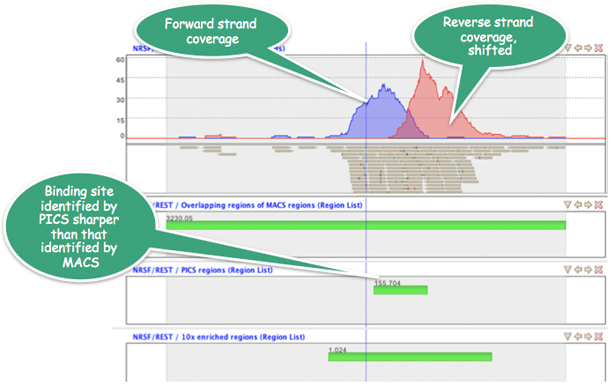
In the NRSF/REST transcription factor binding study, the PICS algorithm in Strand NGS obtains ~1800 putative binding sites, genes around which showed substantial enrichment in neuronal functions.
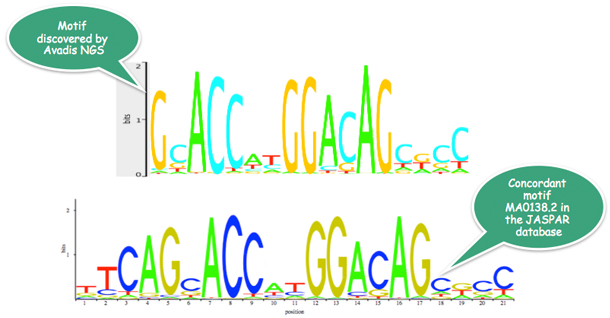
In the NRSF/REST transcription factor binding study, Strand NGS determines the above motif with roughly 1400 matches; this motif is present in the JASPAR database.
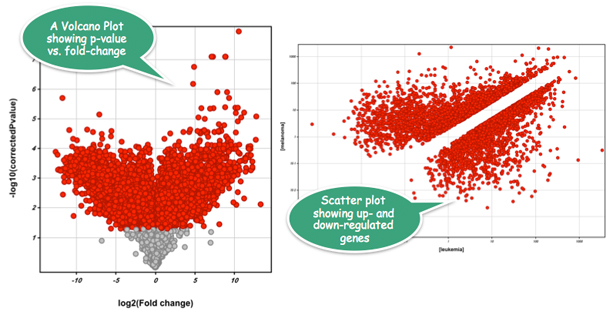
Strand NGS computes gene RPKMs with fractional handling for multiply mapping reads and provides statistical tests based on the Poisson distribution.
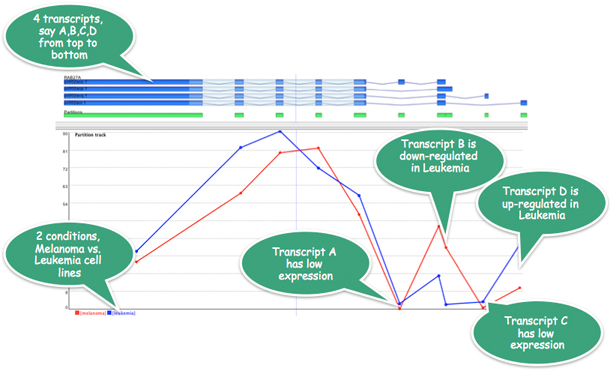
Strand NGS identifies the RAB27A gene to be differentially alternatively spliced when comparing the MEWO Melanoma cell line with the K562 Leukemia cell line
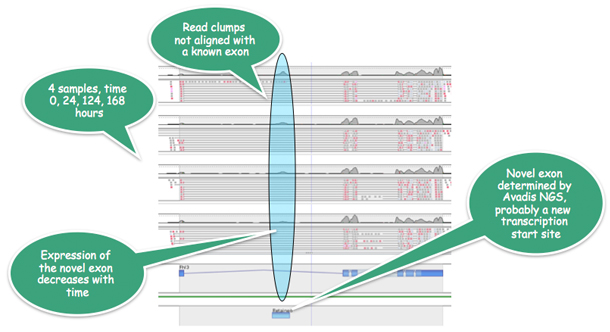
In a mouse myoblast time course study, Strand NGS determines a new exon for the FHL3 gene
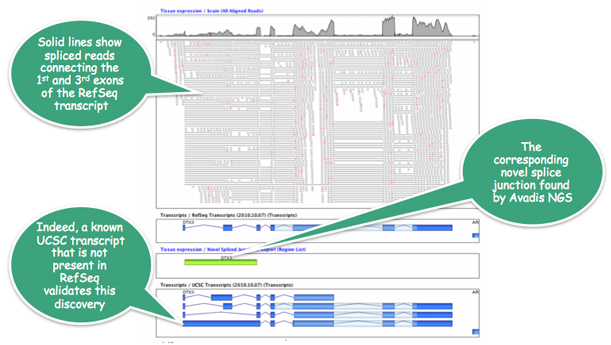
In a brain tissue expression study, Strand NGS determines a new splice junction in the DTX3 gene when considering only RefSeq transcripts; this novel splice junction is corroborated by a UCSC transcript.
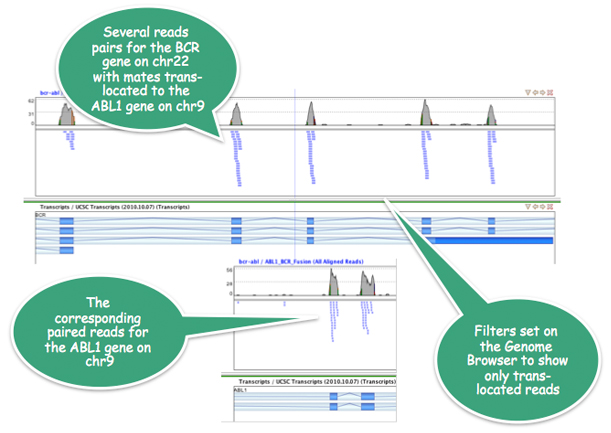
In a K562 Leukemia cell line, Strand NGS confirms the well-known BCR-ABL1 gene fusion.
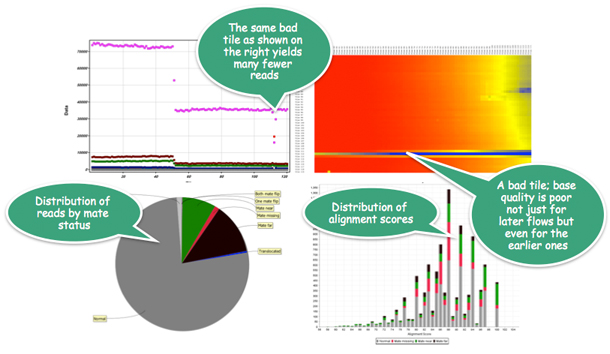
Strand NGS allows viewing reads by lane, tile, alignment score, mapping quality, mate status etc, and also determines on- vs. off-target ratios; in the picture above, Strand NGS determines that reads coming from one of the tiles could be problematic, and allows users to filter them out.
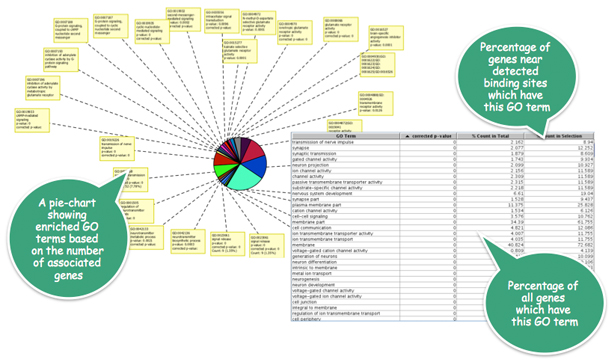
In the NRSF/REST transcription factor binding study, Strand NGS determines genes overlapping the discovered binding regions to be enriched for terms relating to synaptic transmission.
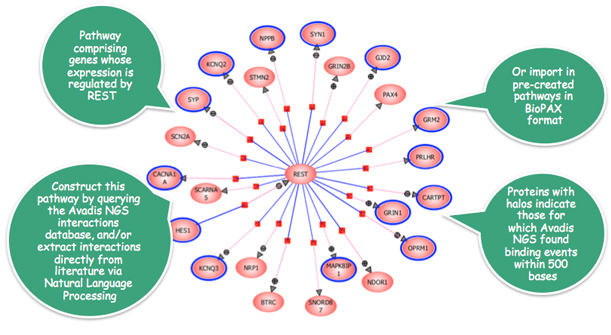
In the NRSF/REST transcription factor binding study, Strand NGS constructs the above interactions map comprising genes whose expression is regulated by NRSF/REST and determines that 14 of the 23 genes have detected binding events within 500 bases of the gene boundary.
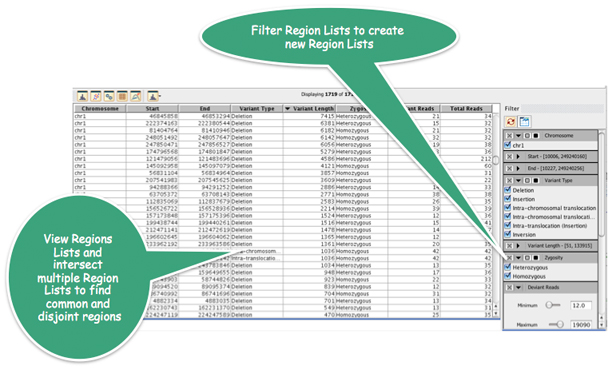
Strand NGS provides various methods to manipulate Region Lists. For instance, create a sub-Region List comprising only homozygous deletions using the filter shown above.
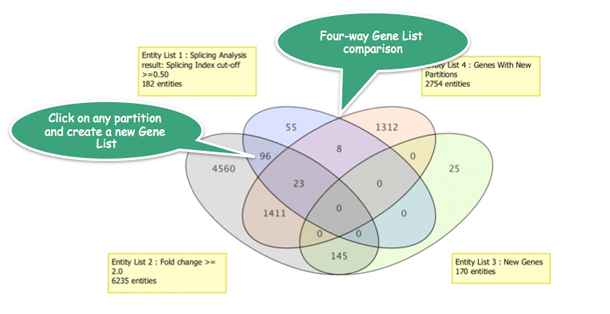
Strand NGS provides various methods to manipulate Gene Lists: create new Gene Lists by selecting genes or via statistical operations, import your own Gene Lists, and even find 4-way intersections as shown above.
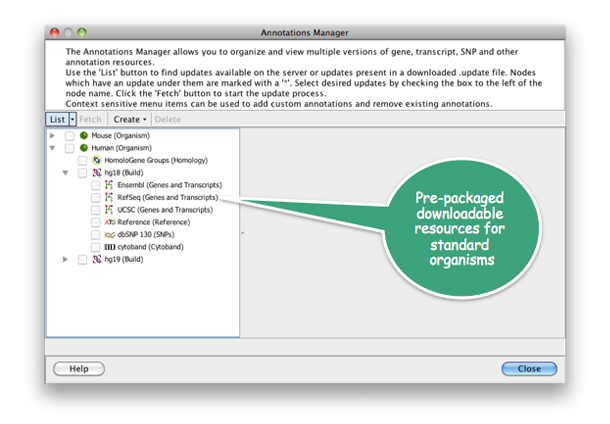
With Strand NGS, simply download all material associated with the desired genomic build and organism with a single click.
Thank you for reading this guide all the way through! If you are interested in trying the software yourself, sign up for a trial license. If you have any questions about a particular feature or experiment workflow, please contact us for more information or register for an interactive webinar.
